-40%
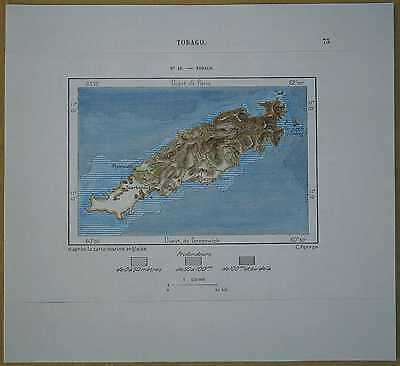
1893 Perron map TOBAGO, REPUBLIC OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO, LESSER ANTILLES (#18)
$ 10.53
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
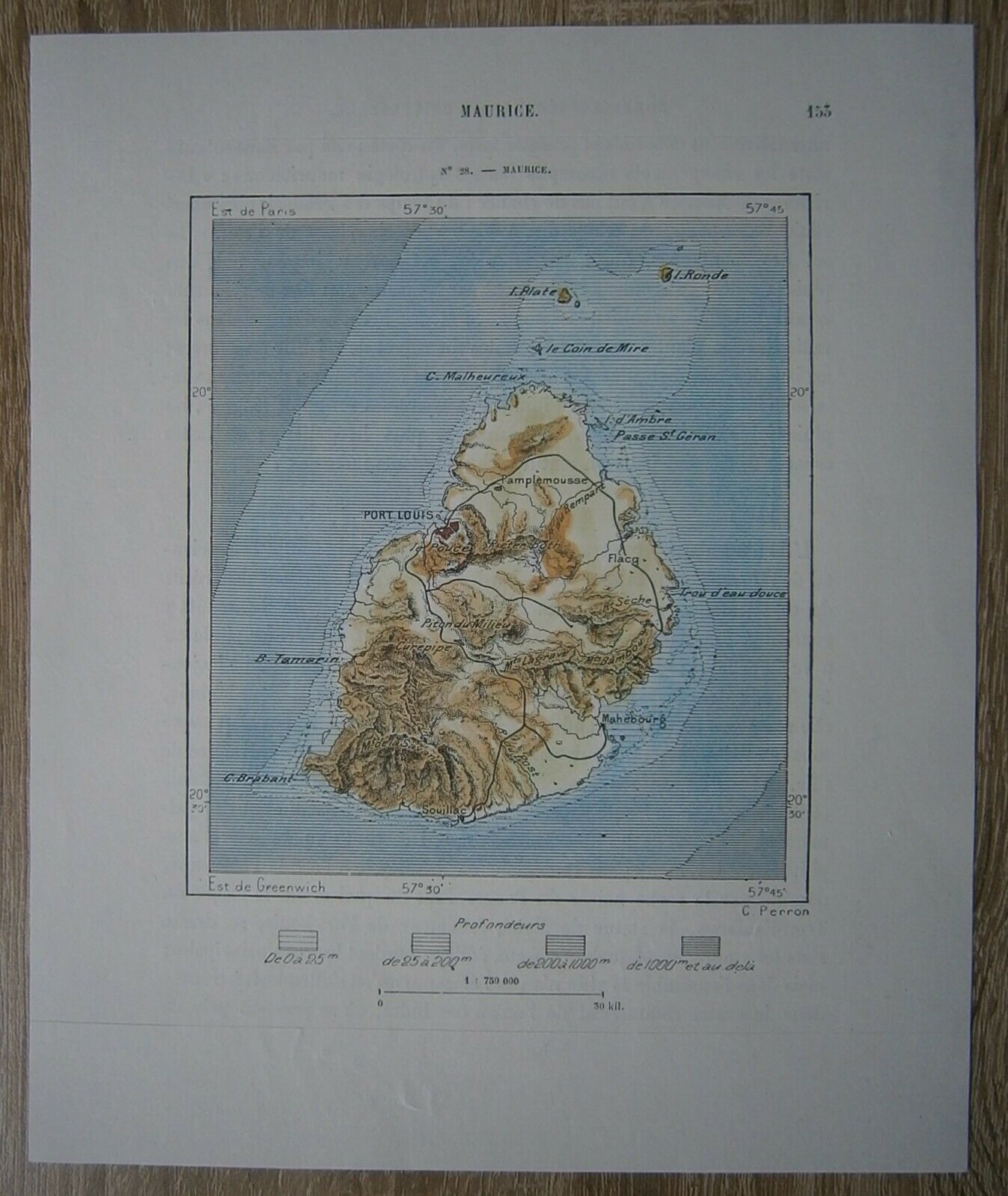
Perron18_0181893 Perron map TOBAGO, REPUBLIC OF TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO, LESSER ANTILLES (#18)
Nice map titled
Tobago,
from wood engraving with fine detail and clear impression, nice hand coloring. Overall size approx. 17 x 15.5 cm, image size approx. 11 x 7.5 cm. From
La Nouvelle Géographie universelle, la terre et les hommes
, 19 vol. (1875-94), great work of Elisee Reclus. Cartographer is Charles Perron.
Tobago
Tobago is an autonomous island within the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the mainland of Trinidad and southeast of Grenada, about 100 miles (160 km) off the coast of northeast Venezuela. According to the earliest English-language source cited in the Oxford English Dictionary, Tobago bore a name that has become the English word tobacco. The national bird of Tobago is the cocrico.
Christopher Columbus first sighted Tobago in 1498. Subsequently, several powers fought over possession of the island.
The original Island Carib population had to defend the island against other Amerindian tribes. Then, during the late 1500s and early 1600s, the natives defended it from European colonists, including 1654, including an attempt by the Courlanders, who colonised the island intermittently between 1637-1690. Over the ensuing years, the Curonians (Duchy of Courland), Dutch, English, French, Spanish and Swedish had caused Tobago to become a focal point in repeated attempts, of colonisation, which led to the island having changed hands 33 times, the most in Caribbean history, before the Treaty of Paris ceded it to the British in 1814. In 1662, the Dutch brothers Adrian and Cornelius Lampsins were granted the title of Barons of Tobago, and ruled until the English captured the island in 1666. Adrian briefly recaptured Tobago in 1673, but was killed in battle when the English, under Sir Tobias Bridge yet again took control of the island.
From about 1672, during the temporary British rule of 1672-1674, Tobago had a period of stability during which plantation culture began. Sugar, cotton and indigo factories sprang up and Africans were imported by the British to work as slaves. The economy flourished. France had abandoned the island to Britain in 1763, and by 1777 Tobago was exporting great quantities of cotton, indigo, rum and sugar. But in 1781, the French re-invaded Tobago, and destroyed the plantations, and forced the British governor to surrender. The island's buoyant economy fell into decline.
In 1814, when the island again came under British control, another phase of successful sugar-production began. But a severe hurricane in 1847, combined with the collapse of plantation underwriters, marked the end of the sugar trade. In 1889 the island became a ward of Trinidad. Without sugar, the islanders had to grow other crops, planting acres of limes, coconuts and cocoa and exporting their produce to Trinidad. In 1963 Hurricane Flora ravaged Tobago, destroying the villages and crops. A restructuring programme followed and attempts were made to diversify the economy. The development of a tourist industry began.
Trinidad and Tobago obtained its independence from the British Empire in 1962 and became a republic in 1976.